600 F - 650 F. Types 316 and 316L are molybdenum-bearing austenitic stainless steel which are more resistant to general corrosion and pittingcrevice corrosion than the conventional chromium nickel austenitic stainless steel such as Type 304.

Hardening After Annealing In Nanostructured 316l Stainless Steel Sciencedirect
Inconel X Spring Temper.

Stress relieve 316 ss. Stress relieving offers several benefits. But I suppose in order to justify it the design would have to be cuttin it pretty close in regards to the service it will be used for. As a general guideline it is advisable that the range 480-900C is avoided.
Stress Relieving 304316 SS CalvinKelly Materials 11 Oct 03 1115 The usual steel stress relieving temperature around 1100F 600C does not relieve much stress in austenitic SS but can make things worse by causing intergranular carbide precipitation. This is particularly apparent for pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride environments. Conditions which cause SCC are.
316 Stainless Steel. Stress relief at temperatures below 750F 400C is an acceptable industry practice but results in only a modest level of stress reduction. For example when a component with high residual stresses is machined the material tends to move during the metal removal operation as the stresses are redistributed.
Heat to 1100-1400 F hold for sufficient time and air cool. These alloys also offer higher creep stress-to-rupture and tensile strength at elevated temperature. Grade 316 is an improved version of CS 304 with the addition of molybdenum and a slightly higher nickel content.
While the 450-750ºF 230-400ºC stress-relief temperatures are recommended for dimensional stability Table 2 there is evidence to suggest that they may not be as effective for plate as using higher temperature that is 1100-1150ºF 590-620ºC that you mention. PWHT of SS would normally only be used to homogenize the microstructure solution annealing. They also offer higher creep stress-rupture and tensile strength at elevated temperature.
Buy Today Get Your Order Fast. 16 hours then reduce to 700 F for 1 hour. Carbon steels may be stress relieved by holding a temperature at 1100 to 1250F 600 to 675C for 1 hour per inch 25 mm of thickness.
Wide Selection of Connectors In Stock at Allied. Stainless Steel 17-7PH or 17-4PH. Stress relieving of Ferritic or martensitic stainless steels will temper weld and heat affected zones.
The corrosion resistance in these alloys is primarily a function of stress relief temperature. Stress relieving is often performed on large or intricate weld sections or on dissimilar weldments composed of low alloy steel welded to stainless steel. 1 presence of halide ion generally chloride 2 residual tensile stresses and 3 environmental temperatures in excess of about 120 F 49 C.
Stress relieving treatments for austenitic stainless steel. There might be some argument for 316 given the way Mo is supposed segregate. Your question on the stress relief of 316L plate is a good one.
This results because of their similarity in nickel content. 700 F - 900 F. Heat to 300-800 F hold for sufficient time and air cool.
Structed of stainless steel. Not generally as stress relief. This makes it suited to use in heavy gauge over.
35 rows Stainless Steel 302. Also known as DINEN designation No. Wide Selection of Connectors In Stock at Allied.
S tainless stee l 316 contains an addition of molybdenum that gives it improved corrosion resistance. 316L the low carbon version of S tainless stee l 316 is immune to grain boundary carbide precipitation sensitisation. The low carbon 304Lor 316L or the stabilised 321or 347 types should not be at risk from corrosion sensitisation during stress relieving treatments.
Buy Today Get Your Order Fast. When the weldment of 316 grade stainless steel is not suitable for complete annealing the residual stress can be moderately lowered below 600 C which makes it. If you are stress relieving it to remove the stresses from the forging you should have done it prior to machining - to avoid sensitization youd probably want to run it up pretty high austenitize it and rapidly cool it through the sensitization range but now that youve machined it distortion during the heat treatment will throw your tolerances out.
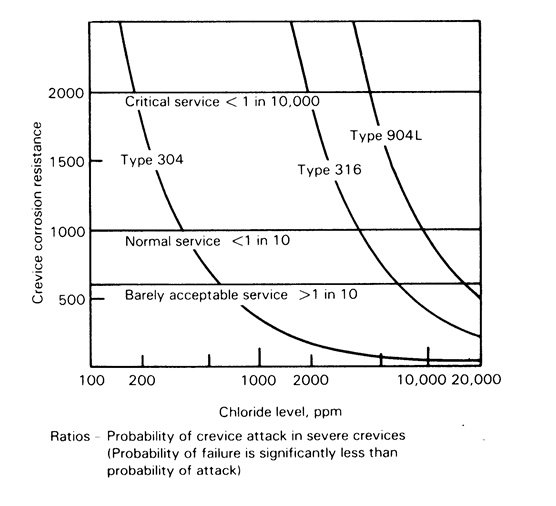
The Type 321 austenitic stainless steel is susceptible to stress corrosion cracking SCC in halides similar to Type 304 stainless steel. The resultant composition of CS 316 gives the steel much increased corrosion. The Type 316 alloys offer excellent resistance to general corrosion and pittingcrevice corrosion which is better than the conventional chromium-nickel austenitic stainless steels such as Type 304.
Stainless Steel - Grade 316 Grade 316 316L Technical Data Summary.

The Microstructure Of The As Received 316 Stainless Steel Ss Observed Download Scientific Diagram

Stainless Steel 316 Alloy Wire International
Grade 316 Stainless Steel Austral Wright

Stress Strain Curves Of Slm 316l And Annealed 316l Tested At 80 K A Download Scientific Diagram

The Microstructure Of The As Received 316 Stainless Steel Ss Observed Download Scientific Diagram

Tensile True Stress Strain Curves Of 316 Ss Polycrystals With 10 Download Scientific Diagram
0 Comments